- Visibility 87 Views
- Downloads 12 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.achr.2020.030
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis –a histomorphological study at a tertiary care centre
- Author Details:
-
Rajeshwari K *
-
N V Dravid
-
Karibassappa G. N
-
Chakor Rokade
Introduction
Granulomatous dermatitis are hetreogenous group of diseases that differ in pathogenesis, clinical and histopathological presentations.[1] Granulomatous dermatitis often presents as a diagnostic challenge even to the most experienced dermatopathologist. It forms a common and intriguing problem in day to day routine practice. Arrival at an exact and appropriate diagnosis is mandatory for successful treatment. Histopathological examination remains a time tested tool for establishing a correct diagnosis in various diseases of organ system of the body.[2]
Clinically granulomatous dermatitis are poorly defined, they are characterized by infiltrated lesions showing apple jelly - like hue on diascopy. Histopathologically according to A. B Ackerman, it is defined as any inflammation to be considered as granulomatous, atleast 50% of infiltrate should be made up of histiocytes/ macrophages.[3]
The classification of granulomatous dermatitis is mainly based on pathogenesis and therefore has been broadly classified as infectious granulomatous dermatitis and non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis.[4]
Infectious granulomatous dermatitis are those with evidence of underlying infectious agent where as non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis are a part or associated with systemic diseases or neoplastic disorders and mimic granulomatous lesion on histopathology.[5]
Clinical lesions of skin often reveal surprising underlying pathology. An identical histopathological pattern may be produced by several cases and conversely a single cause may produce several histological patterns.[6]
Hence all the skin lesions diagnosed clinically should undergo histopathological examination with routine haematoxylin and eosin along with other special stains, that might help in identifying the type of the granuloma.[7]
It is very essential to differentiate between infectious and non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis as the management and therapeutic interventions differs in both though presents with similar clinical and histopathological findings. Hence the detailed clinical and thorough histopathological examination is required for accurate diagnosis.
Hence, giving importance to non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis the present study was undertaken to study the prevalence and an attempt to study in detail the clinical and histomorphological presentations in non- infectious granulomatous dermatitis.
Materials and Methods
The present study is a retrospective type of analytical study. All the skin biopsies with the granulomatous reaction diagnosed clinically and histopathologically were reviewed and assessed in detail. The study was carried out in the department of pathology, over a period of 5 years (Jan 2011-Jan 2016). Complete clinical and relevant history was recorded. Following eligible criteria was adopted in our study
Inclusion criteria
All type of skin biopsies diagnosed to have non-infectious granulomatous reaction pattern
Exclusion criteria
All biopsies not diagnosed clinically to have non-infectious granulomatous lesion, poorly preserved and inadequate skin biopsies.
Patients diagnosed clinically with a non-infectious granulomatous reaction were selected for the study. Samples were collected employing punch biopsy measuring 4 mm size under aseptic measures. Biopsy samples from each patient were fixed in 10% buffered neutral formalin and then dehydrated in a graded series of ethanol and embedded in paraffin. Sections were stained with Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and relevant special stain like Periodic acid Schiff (PAS), colloidal iron, Giemsa, Alcian blue etc. were done and studied under the light microscope .
Results
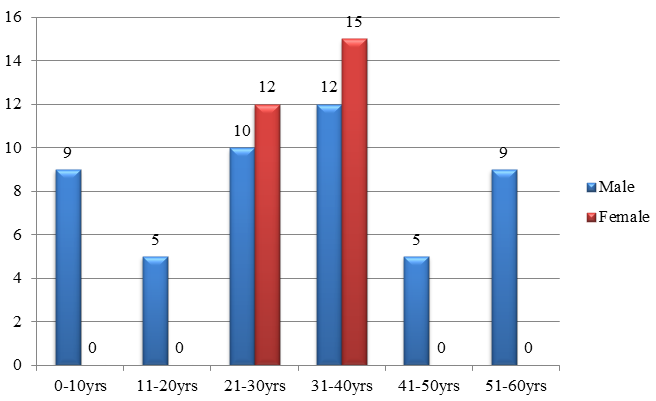
In the present study a total of 2,690 skin biopsies were received during the study period of 5 year. Out of them 314 showed granulomatous reaction pattern. Among them 237 were infectious granulomatous dermatitis and 77 were non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis. Among the 77 cases of non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis 50 cases (65%) were male and 27 cases (35%) were female. The age range of the patient was between 6-70 years. The maximum number of cases was in the fourth decade of life (Graph1). Out of total 77 cases maximum numbers of biopsies of were from head and neck region in 32 cases accounting for 41.6% of cases. 14 cases (18.24%) were from lower limb, 6 cases (7.5%) were from upper limb and three cases (3.6%) from chest, abdomen and back. Site were not mentioned in 22 (29.1%) cases.
Out of the total 77 cases 45 (58.44 %) showed mixed cell granulomas. 19 cases (24.67%) showed palisading granulomas, 10 cases (13%) form non-specific/ miscellaneous group and three cases (3.9%) of epithelioid granulomas without necrosis as shown in ([Table 1]). Details of histopathological and histomorphological features of granulomatous lesions of skin are given in [Table 2], [Table 3].
| No | Granulomatous type | No of cases | % of cases |
| 1 | Mixed inflammatory type | 45 | 58.44% |
| 2 | Palisading type | 19 | 24.67% |
| 3 | Non-specific granulomas /miscellaneous | 10 | 13% |
| 4 | Epithelioid cell granuloma without necrosis | 3 | 3.9% |
| Total | 77 | 100% |
| S.No | Histopathological diagnosis | Number of cases | % of cases |
| 1 | Foreign body granuloma | 25 | 33.07% |
| 2 | Rheumatic nodule | 11 | 14.3% |
| 3 | Suture granuloma | 9 | 11.7% |
| 4 | Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis | 6 | 7.8% |
| 5 | Granuloma annulare | 5 | 6.5% |
| 6 | Discoid lupus erythematous | 4 | 5.2% |
| 7 | Necrobiosis Lipidioca | 3 | 3.9% |
| 8 | Erythema nodosum | 3 | 3.9% |
| 9 | Erythema annulare centrifugum | 3 | 3.9% |
| 10 | Granulomatous chelitis | 3 | 3.9% |
| 11 | Chronic granulomatous Vasculitis | 2 | 2.6% |
| 12 | Papular Xanthoma | 2 | 2.6% |
| 13 | Morphea | 1 | 1.3% |
| Total | 77 | 100% |
| S. No | Histopathological Diagnosis | Type of granuloma | Location of granuloma | Pattern of Distribution | Epidermal changes |
| 1 | Foreign body granuloma (25) | Mixed | Reticular dermis | Nodular | - |
| 2 | Rheumatic nodule (11) | Palisading | Papillary and Reticular dermis | Nodular | - |
| 3 | Suture granuloma (9) | Mixed | Reticular dermis | Nodular | - |
| 4 | Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis (6) | Miscellaneous | Reticular dermis | Interstitial | Spongiosis |
| 5 | Granuloma annulare (5) | palisading | Papillary and Reticular dermis | Interstitial | - |
| 6 | Discoid lupus erythematous (4) | Mixed | Papillary and Reticular dermis | Nodular | Acanthosis /atrophic/ hyperkeratosis |
| 7 | Necrobiosis Lipidioca (3) | Palisading | Reticular dermis | Interstitial | Normal/ atrophic/ hyperkeratosis |
| 8 | Erythema nodosum (3) | Mixed | Reticular dermis | Nodular | - |
| 9 | Erythema annulare centrifugum (3) | Mixed | Papillary (2) and Reticular dermis (1) | Nodular | Parakeratosis, spongiosis and microvesiculation |
| 10 | Granulomatous chelitis (3) | Epithelioid granuloma without necrosis | Papillary (1) and Reticular dermis (2) | Nodular | - |
| 11 | Chronic granulomatous Vasculitis (2) | Miscellaneous | Reticular dermis | Nodular | - |
| 12 | Papular Xanthoma (2) | Miscellaneous | Papillary (1) and Reticular dermis (1) | Nodular | Atrophic |
| 13 | Morphea (1) | Mixed | Reticular dermis | Nodular | Atrophic |
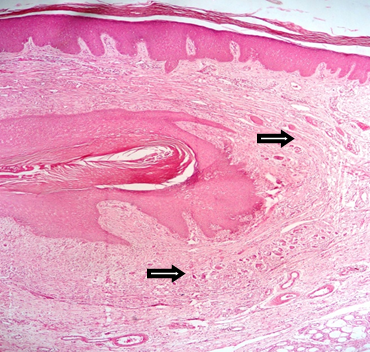
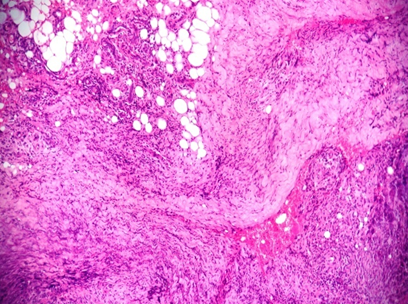
Among the 45 cases of mixed cell garanulomas, it is further sub classified. In the present study maximum number of cases of mixed cell granulomas is foreign body granuloma accounting for 32.46% of cases. Histopathologically foreign body granulomas shows foreign material surrounded by histiocytes, foreign body giant cells , lymphocytes and plasma cells ([Figure 2]), followed by suture granuloma in 11.7% of the cases ([Figure 3]) Discoid lupus erythematous accounting for 5.2 % of cases ([Figure 4] ) erythema nodosum and erythema annular centrifugum each accounting for 3.9 % of cases and morphoea seen in 1.3% cases of the cases.
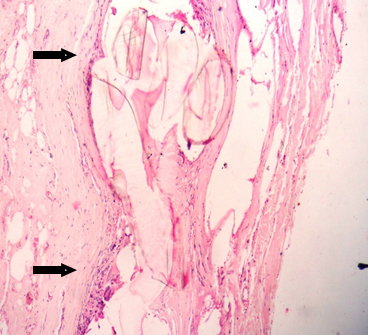
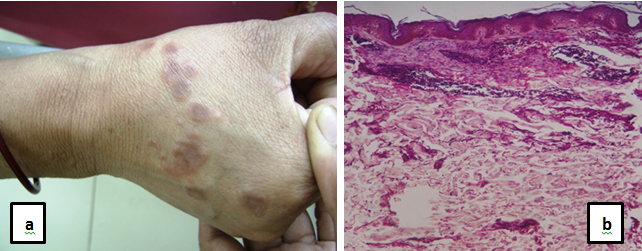
Second common type of non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis observed was palisading type of granulomas, accounting for 24.67 % of the cases. Among these majority were rheumatoid nodule accounting for 14.3% of the cases ([Figure 5]), followed by granuloma annulare accounting for 6.5% of the cases ([Figure 6]a,b) and necrobiosis lipoidica accounting for 3.9 % of the cases ([Figure 7] ).
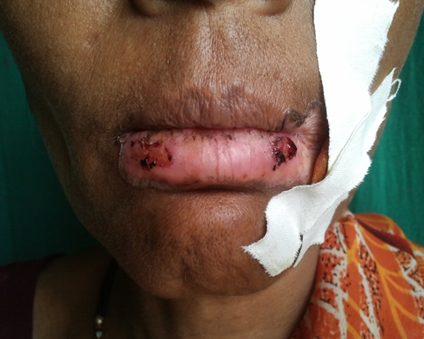
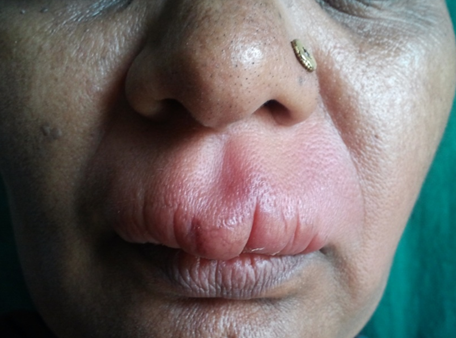
Non-specific granulomas/miscellaneous group constitute 13 % of the non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis. It includes interstitial granulomatous dermatitis accounting for 7.8% followed by chronic granulomatous vasculitis and papular xanthoma each constituting of 2.6% of the cases. The other group includes epithelioid cell granuloma without necrosis includes granulomatous chelitis accounting for 3.9% of the cases([Figure 8]).

Discussion
Non- infectious granulomatous dermatitis is distinct group of reactive inflammatory conditions. They are difficult to diagnose and distinguish both clinically and histologically, hence offer a diagnostic challenge to both dermatologist and histopathologist.[8] Non- infectious granulomatous dermatitis are known for polymorphic, clinical and histological presentations with chronic and undulating disease courses having resistant to therapeutic interventions.[9]
Literature search reveal limited data available on non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis that is necessary to establish the treatment algorithms for non- infectious granulomatous dermatitis. There is lack of randomized controlled studies published on non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis.
Hence, an attempt is made, to take up the present study on non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis. The study reveals details of clinical presentations, histopathological and histomorphological features in non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis.
The exact pathogenesis is not fully understood, it is thought that pathogenetic mechanism involved may be due to reaction pattern caused due to immunogenic stimulus. This immunogenic stimulates the antigen presenting cells to release large amount of TNF – alpha and interleukins. Hence most of the non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis is treated with immunosuppressants and immunomodulatory therapy.[10]
The diagnosis of non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis requires detailed medical history, clinical examination and histopathological evaluation and thorough proper clinicopathologic correlation. Recent ancillary techniques in diagnosis include Immunohistochemistry and molecular genetics for accurate diagnosis.
The dermoscopy helps in diagnosing the dermal granuloma and also the various vascular patterns that help in differential diagnosis.[11] Histopathological examination requires detail examination of 1.Location of granuloma superficial/deep. 2. Pattern of distribution of granuloma – interstitial/nodular. 3. Intensity. 4. Composition of dermal infiltrate – lymphocytes plasma cells, histiocytes and type of giant cells.[12]
In the present study majority of the cases occurred in the third decade. Our present findings are in concordance with Dhar’s study [2] and Grover’s study.[13] In our study, male are more susceptible to develop non-infectious granulomatous lesions. Similar findings are seen with Dhar’s study [2] , Gautam’s study[14] and Grover’s study. [13]
In our study, foreign body granuloma was most commonly observed finding accounting for 22.07% of the cases and our findings are in consistent with Mohan’s study, [15] Gautam’s study[14] and Grover’s study. [13]
Most of the foreign body granuloma in our study is due to keratin material released due to rupture of epidermoid cyst and also due to dermal deposition of calcium salts with foreign body reaction to it.
In our study we found 14.3 % of the cases of rheumatic nodule, whereas Mohan’s study showed 2.8% of the cases[15] and Grover ’s study observed 3.4% of the cases.[13]The cases are high in our study may be due to high detection rate at our centre, as our centre has attachment to Rheumatology hospital.
It is observed that rheumatoid nodules are seen in 20-25% of the patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting as most common extra articular manifestation seen due to immune complex deposition.[16], [17] The special stain used to diagnosis rheumatoid nodule is Periodic acid Schiff (PAS) stain, positive showing large amounts of fibrin. The close differential diagnosis includes subcutaneous granuloma annulare that is mucin positive.
Present study noted 11.7% of the cases of suture granuloma. Literature review as shown that suture granuloma are very common with silk suture, which is non-absorbable with incidence of 0.6 -7.1%. Suture granulomas are very common with surface surgeries and presents in early post- operative period. Most of the suture granulomas mimics as neoplastic lesion on radiological evaluation.[18] Our study encountered interstitial granulomatous dermatitis accounting for 7.8% of the cases. It is associated with various systemic diseases having autoimmune and immune complex formation etiology like Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematous and thyroiditis. It is also noted that it is associated with malignant disease like lymphoproliferative
disorders.[19], [20], [21] Clinically patient presents with plaques, papules or cord like indurations. Histopathologically dermis shows interstitial infiltrate of macrophages, lymphocytes and neutrophils around single collagen fibres.
Our study found Granuloma annulare (GA) accounting for 6.5% of the cases. Our findings are in accordance with Gautam’s[14] study and Mohan’s study.[15]
Clinically presents with macules or localized annular lesions. Granuloma annulare
has two types of manifestation that includes 1. Subcutaneous GA. 2. Perforating GA. [4] In our study all the cases of GA were of Subcutaneous GA .Cytochemical stains like colloidal iron and alcian blue helps in diagnosing the mucin presence. Immunohistochemistry CD 68, CD 163 helps in confirming the diagnosis of GA. Treatment includes 50% of the cases show spontaneous remissions within 2yrs the rest are treated with corticosteroids and immunomodulatory therapy.[5]
In our study we observed four cases of Discoid lupus erythematous (DLE) accounting for 5.2% of the cases. DLE is the most common cutaneous form of lupus erythematous. Litrature reveals 23-28% presents with cutaneous form. The diagnosis of DLE is confirmed by clinical presentation, histopathology and special stains like Periodic acid Schiff (PAS) showing the thickening of basement membrane and alcian blue or colloidal iron for mucin. Direct immunoflouroscent test showing IgG, IgM , Ig A and complement at dermoepidermal junction. Antibody titres help in confirming the diagnosis.[22]
Present study noted three cases necrobiosis lipoidica (NL) accounting for 3.9% of the cases. Our findings are in consistent with Grover’s study[13] accounting for 6.9% of the cases. Studies have shown that NL show association with systemic diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases like hypertension and obesity in 58% of patients and thyroid diseases upto 24% of association is seen.[5]
Our study showed three cases of erythema nodosum (EN) accounting for 3.9% of the cases and our findings are in accordance with Grover ’s study[13] accounting for 6.9% of the cases. Erythema nodosum also called as granulomatous panniculitis. Clinically presents as red painful bilateral symmetrical nodules. Histopathologically it presents as marked septal fibrosis, infiltrated with neutrophils, lymphocytes histiocytes, granulomas and giant cells.
We found three cases of Erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC) in our study accounting for 3.9% of the cases. EAC is an idiopathic skin disorder clinically presents as ring shaped lesions with central clearing. Histopathologically it shows spongiosis, parakeratosis and microvesiculation in the epidermis. Dermis shows perivasular lymphohistiocytic infiltrates.
In order to provide accurate diagnosis of granulomatous lesions of skin, cooperation between clinician and pathologist is very important in the field of dermatology for the greatest benefit from the biopsy. The clinician should provide detailed clinical history which includes age, sex, sit, type and colour of skin lesions with list of differential clinical diagnosis.[23]
Conclusion
To understand the clinical behavior of non-infectious granulomatous dermatitis, it is very essential to have knowledge of the histopathological features of the dermatitis. Recognition at early stages of the inflammation is important for effective therapy. Hence early and accurate diagnosis can be done with combined approach of both clinician and pathologist for appropriate therapy and outcome of specific diseases.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
References
- M Tronnier, H H Wolff, H Kerl, C Garbe, L Cerroni, H H Wolff. Dermatosen mit granulomatöser Entzündung. Histopathologie der Haut 2003. [Google Scholar]
- S Dhar. Histopathological features of granulomatous skin diseases: an analysis of 22 skin biopsies. Indian J Dermatol 2002. [Google Scholar]
- A B Ackerman. Histologic diagnosis of inflammatory skin diseases. 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Michael Tronnier, Christina Mitteldorf. Histologic features of granulomatous skin diseases. Part 1: Non-infectious granulomatous disorders. JDDG 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Andrea Schmitt, Andreas Volz. Non‐infectious granulomatous dermatoses. JDDG 2019. [Google Scholar]
- M T Zaim, R T Brodell, D R Pokorney. Non-neoplastic inflammatory dermatoses: A clinical pathologic correlative approach. Mod Pathol 1990. [Google Scholar]
- E E David, ’ Lever. Lever’s Histopathology of the skin. Part 3: Disease listings categorized by site, pattern and cytology 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Elena Balestreire Hawryluk, Leonid Izikson, Joseph C. English. Non-Infectious Granulomatous Diseases of the Skin and their Associated Systemic Diseases. Am J Clin Dermatol 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ari M Goldminz, Alice B G. Non-infectious granunulomatous dermattides: a Review of 8 disorders. Semin Cutan Med Surg 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Melanie Peckruhn, Jörg Tittelbach, Peter Elsner. Update: Treatment of necrobiosis lipoidica. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Enzo Errichetti, Giuseppe Stinco. Dermatoscopy of Granulomatous Disorders. Dermatol Clin 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Michael Tronnier, Christina Mitteldorf. Histologic features of granulomatous skin diseases. Part 1: Non-infectious granulomatous disorders. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sumit Grover, ShubangiVinayak Agale, Grace D′Costa, ArvindG Valand. Noninfectious granulomatous dermatoses: A puzzle for dermatologists and histopathologists. J Med Soc 2017. [Google Scholar]
- K Gautam, R R Pai, S Bhat. Granulomatous lesions of the skin. J Pathol Nepal 2011. [Google Scholar]
- H Mohan, A Bal, G P Dhami. Non - Infectious granulomatous dermatitis: A clinico pathological study. J Cutan Pathol 2006. [Google Scholar]
- C. M. Magro, A. N. Crowson. The spectrum of cutaneous lesions in rheumatoid arthritis: a clinical and pathological study of 43 patients. J Cutan Pathol 2003. [Google Scholar]
- E M Veys, F De Keyser. Rheumatoid nodules: differential diagnosis and immunohistological findings.. Ann Rheumatic Dis 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Santosh Kumar Singh, Narayan Kannan, Rajnish Talwar, Arvind Kumar Tyagi, Renu Madan, Pradeep Jaiswal. Suture granuloma: a rare differential diagnosis of residual/recurrent gastrointestinal stromal tumor of stomach. Int Cancer Conf J 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bevin Bhoyrul, Calum Lyon. Crohn's disease of the vulva: A prospective study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018. [Google Scholar]
- M A Rosenbach, K A Wanat, A Reisenauer. Dermatology; non-infectious granulomas. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- M M Woody, A C Holliday, Acp Gavino. Metastatic vulvovaginal Crohn disease inthe setting of well-controlled intestinal disease. Cutis 2018. [Google Scholar]
- E David. Lever’s Histopathology of the skin. Connective tissue diseases 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus H, Mehregan AH. A Guide to Dermatopathology. 3rdedn. 1981. [Google Scholar]
